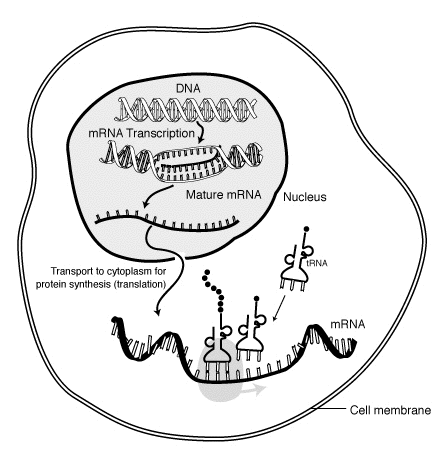
 In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a molecule in cells that carries codes from the DNA in the nucleus to the sites of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm (the ribosomes). Each mRNA molecule encodes information for one protein.
Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a molecule in cells that carries codes from the DNA in the nucleus to the sites of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm (the ribosomes). Each mRNA molecule encodes information for one protein.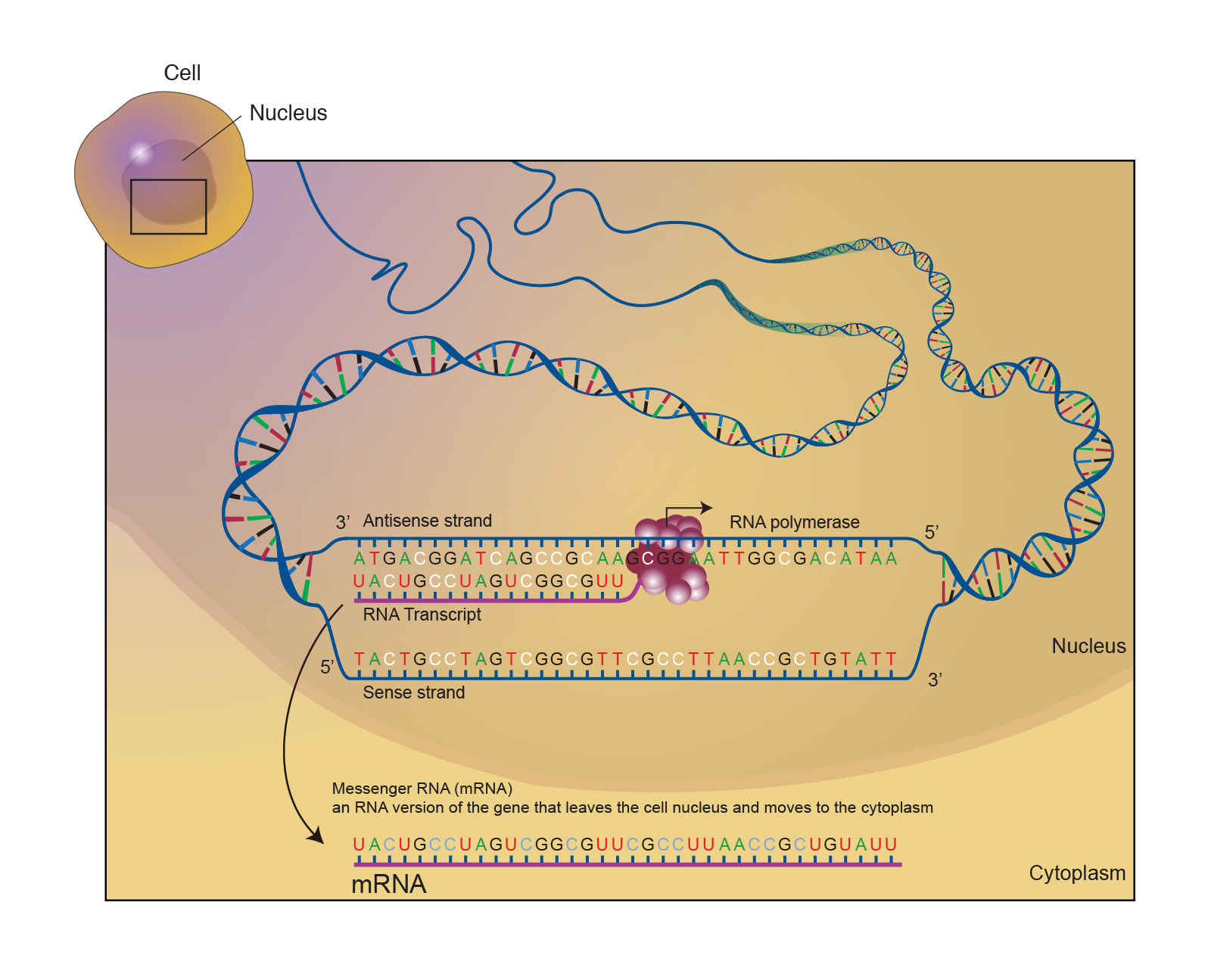 Messenger RNA (abbreviated mRNA) is a type of single-stranded RNA involved in protein synthesis. mRNA is made from a DNA template during the process of transcription.
Messenger RNA (abbreviated mRNA) is a type of single-stranded RNA involved in protein synthesis. mRNA is made from a DNA template during the process of transcription.